The balance sheet is like a financial snapshot of a company at a specific point in time. Notes receivable represent money owed to the company in the form of promises to pay (IOUs) from customers who have bought stuff on credit. Now, let’s take a peek at how notes receivable cozy up on the balance https://www.bookstime.com/ sheet. They usually hang out in the current assets section, arm-in-arm with their buddies like cash and inventory. Among the myriad of current assets, one particularly intriguing one is notes receivable.
Impairment and bad debt considerations

Cash Equivalents – Cash equivalents are investments that are so closely related to cash and so easily converted into cash, they might as well be currency. T-bills can be exchanged for cash at any point with no risk of losing their value. In addition to what you’ve already learned about assets and liabilities, and their potential categories, there are a couple of other points to understand about assets.
- When a promissory note is accepted, it is accounted as a note receivable, which becomes a current asset if it is a short-term or a payment that shall be paid within one year.
- Accounts Receivable represents short-term credit, often with terms like 1/10 Net 30, meaning payment is expected within 30 days.
- In other words, the property itself acts as a security for the mortgage loan, and the value of the property will parallel the value of the loan.
- Therefore, debiting the notes receivable account reflects this increase in assets.
- For this reason, notes are negotiable instruments the same as cheques and bank drafts.
What Type of Account is Interest Income?
The accounting for a lease depends on whether it are notes receivable current assets is a capital lease or an operating lease. Notes Payable with repayment terms exceeding one year are classified as Non-Current Liabilities. Notes Receivable is positioned under Assets as a resource owned, representing a future claim to cash.

Comparing Current and Noncurrent Assets: Key Differences
Since notes receivable have a longer duration than accounts receivable, they usually require the maker to pay interest in addition to the principle, at the maturity of the note. Interest receivable is recognized on the balance sheet in addition to the face value of notes receivable. how is sales tax calculated It’s important to note that not all Notes Receivable will qualify as current assets. If there is uncertainty about when payment will be received beyond one year or if there are restrictions on collecting payments before maturity date, then it would not be classified as a current asset.
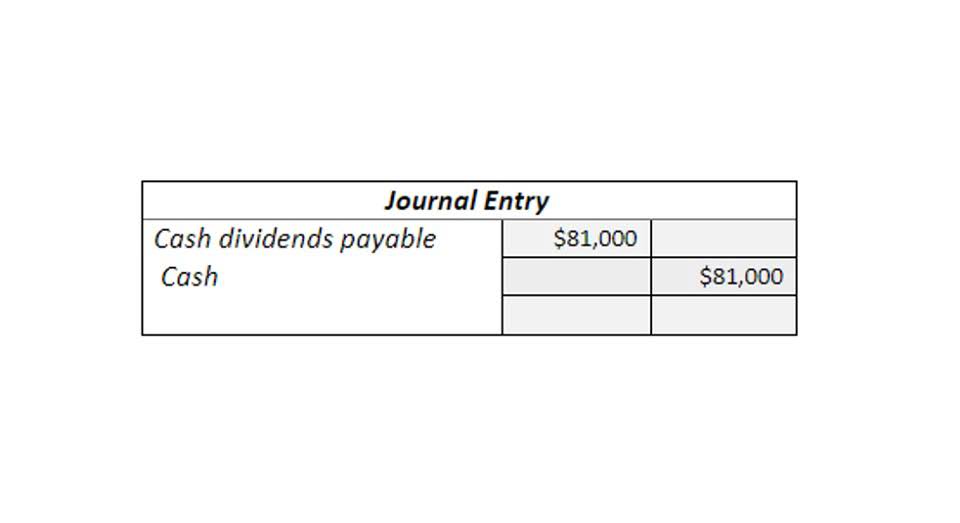
- In turn, Savoy’s net income will be the $16,000 revenue reduced by any uncollectible receivables, since it now has assumed the risks/rewards and control of these receivables.
- It’s sometimes helpful to use a “T” account when determining the proper allowance amount.
- Some of these companies recovered through good management, and cash flows returned.
- At the maturity date of a note, the maker is responsible for the principal plus interest.
- Accounts Receivable – Accounts receivable is essentially a short-term loan to customers and vendors who purchase goods on account.
- This Principal amount is the basis upon which interest calculations are performed.
In accounting, notes receivable represent money owed to a business, and when they increase, it signifies that the business is expecting to receive more cash from customers or borrowers. Therefore, debiting the notes receivable account reflects this increase in assets. Although they provide value, they cannot be readily converted to cash within a year.
Revenue Recognition
Thus, the receivables account must be adjusted to reflect the amount of receivables that management expects to convert into cash in the current period. While notes receivable and notes payable are related, they are not the same thing. Notes payable, on the other hand, indicate the monetary obligation the maker has to the payee. One major difference between notes receivable and accounts receivable is that notes receivable are in effect a promissory note. The promissory note is a legally binding document that compels the customer to pay.

If the note receivable is due within one year or the company’s operating cycle (whichever is longer), it is classified as a current asset. If the maturity date extends beyond that period, it is classified as a non-current asset. This classification ensures an accurate representation of the asset’s value on the balance sheet. It distinguishes between amounts expected to be realized within the next operating cycle (current assets) and those not expected to be realized within that timeframe (noncurrent assets).